2 Minutes Read
Listen to the Blog
Constraints & Responsive Design in Figma: Flexible UI for All Screens
1:50
Make your designs flexible for different screen sizes.
1. Why Constraints Are Key for Responsive Design
Constraints in Figma control how elements behave when frames resize, allowing you to:
- Build flexible layouts that work on desktop, tablet, and mobile
- Maintain alignment, spacing, and scale across devices
- Reduce manual adjustments when adapting designs
- Improve workflow efficiency for multi-screen projects
Tip: Combine constraints with Auto Layout and Layout Grids for fully responsive designs.
2. Setting Constraints
- Select a layer or component inside a frame.
- In the right-hand panel, locate Constraints.
- Choose options:
- Left, Right, Top, Bottom: Stick elements to specific edges
- Center: Keep elements centered horizontally/vertically
- Scale: Resize element proportionally with the frame
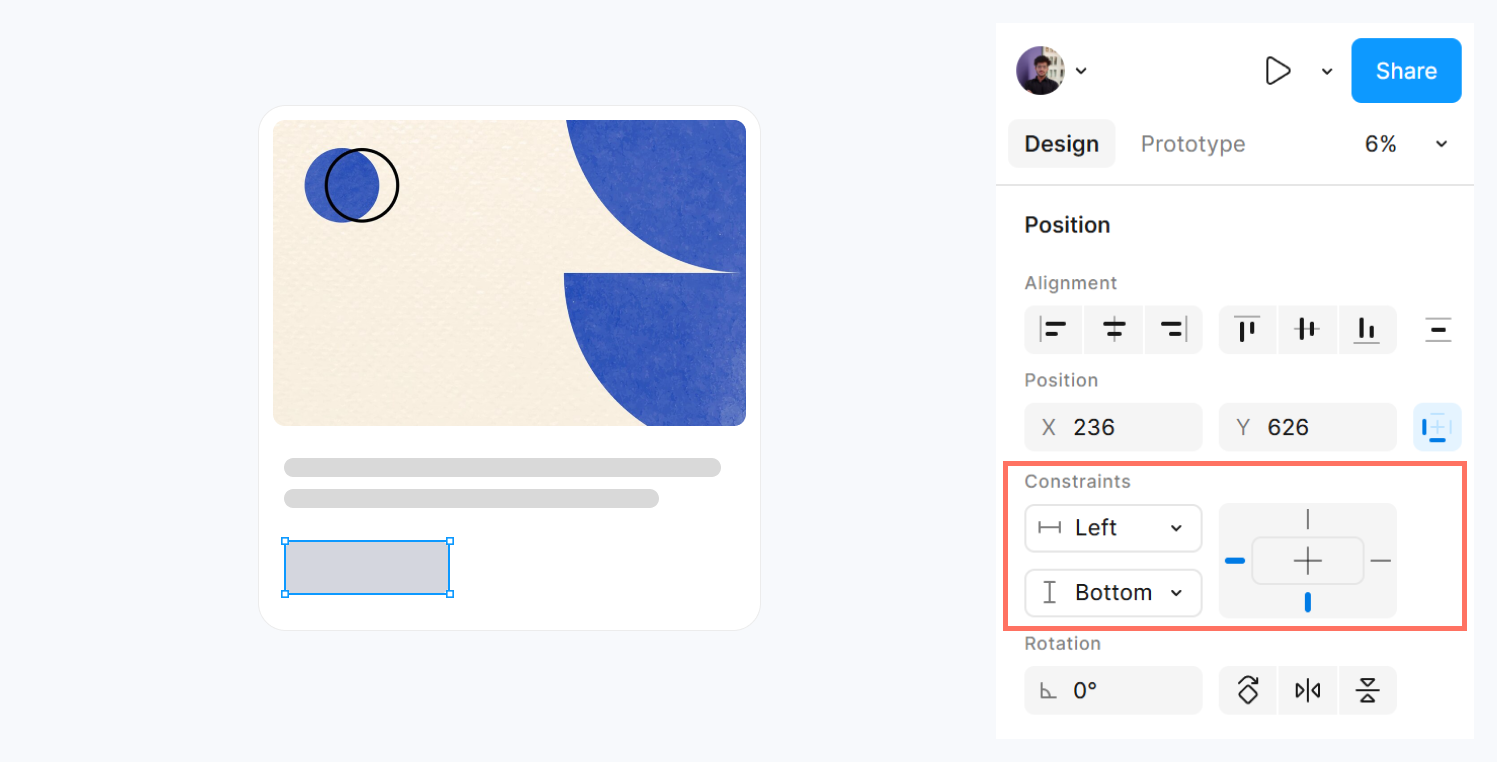
Tip: Use different constraints for nested elements to make cards, buttons, and headers adapt automatically.
3. Combining Constraints with Frames
- Fixed Frame: Elements maintain exact size and position → not responsive
- Resizable Frame: Elements adapt based on constraints → responsive layout
- Test by resizing the frame to see elements move/scale accordingly
Example: Navbar logo constrained to left, menu items constrained to right → layout adapts across desktop, tablet, and mobile.
4. Practical Examples
Example 1: Buttons
- Constrain buttons to the bottom-right corner
- Buttons maintain position when resizing container
Example 2: Cards
- Image constrained to scale proportionally
- Text constrained to top/left remains readable
Example 3: Hero Section
- Headline centered horizontally
- CTA button constrained to bottom
- Background image scaled responsive across screen sizes
Tip: Combine constraints + Auto Layout + Variants for responsive, multi-state components.



.png)



%201.png?width=1016&height=912&name=image%20(54)%201.png)