Listen to the Blog
Creating easy-to-navigate, aesthetically appealing user interfaces (UI) and delivering remarkable user experiences (UX) are integral to meeting user demands and high conversion ratesensuring. UI/UX developers play a significant role in helping to build and run digital goods that will attract and engage people. A road map is important to help you become an expert in this field of study.
Those looking for excellence in the ever-changing world of digital interactions look for a road map that not only guides but also motivates potential UI/UX designers. This is your comprehensive guide that explains beginners about UI/UX design and how they can become successful designers in this field.
Well, there is nothing that you need to fear about, fellow coder! This guide will offer you 7 practical tips to propel your web development skills to new heights. But before that, let's understand the different types of web developments. This way, you can know which category you fall in.
Understanding UI/UX Design
A UX/UI design is the procedure of creating the interface, enhancing navigation, and simplifying the process for users to explore and find the relevant elements of a good or service. It incorporates design principles alongside user experience to produce user interfaces that are easy to use, quickly deliver what consumers want, look great, are simple, and lead to an overall satisfying user experience. While often used together, UI and UX are terms that have different meanings.
User Interface(UI)
User Interface (UI) is more focused on design and tends to focus on the appearance and feel of the product. The main aim is to create an interactive platform with essential features, including buttons, color schemes, typography, icons, and graphics.
User Experience(UX)
The user experience, commonly called UX, refers to how someone feels about using a particular service, product, or website until they accomplish their goal. It's a more comprehensive term that includes a person's emotions towards a product as well as the activities that follow after the encounter. It all comes down to the feelings that are created when using a digital product.
Why do Companies Hire UI/UX Designers for Products?
The objective behind good UI/UX design is to create products that are capable of problem-solving and are user-friendly. This holds significance for both companies and end consumers.
In business, UI/UX design is important for identifying customer needs and ensuring a satisfying user experience, which creates sales, revenue, customer loyalty, and engagement. It also helps develop a company's brand name through products and experiences that promote emotions and a sense of familiarity, thereby building up a loyal customer base.
From the user's perspective, UI/UX design simplifies technology and provides solutions to common issues, contributing to a more accessible and inclusive world when done well.
UI/UX Designer's key principles
Effective product development requires some principles by UX/UI designers which lead to a positive user experience. Some of the major ones are:
User-Centricity
UI/UX design should start with understanding the user; therefore, user research comes first in designing processes. This will ensure that produced goods meet market needs while addressing consumer problems, hence leading to a more consumer-oriented way of creating goods.
Usability
Usability is the process of designing and optimizing a product for goal completion. High usability ensures easy and quick task completion for target consumers, while low usability scores make the product difficult to use.
Accessibility
The accessibility principle considers the accessibility of a good or service to all users, identifying potential accessibility issues and designing solutions to address them. It is particularly essential when considering users with limitations so the platform can be used by everyone easily.
Information Architecture
Information architecture, or IA, considers the organization, structuring, and labeling of data and content within a digital product. Its goal is to help users locate the information they need to complete specific tasks.
Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy refers to the arrangement of elements on a page or screen, while information architecture manages the overall hierarchy of information throughout a product. Significant parts are often displayed in higher font sizes or bolder colors, enhancing the visual hierarchy and directing users' attention to specific areas.
Consistency
Consistency is essential in meeting consumer expectations and fostering familiarity. Designers can simplify user interfaces by incorporating consistent patterns and elements across their products, leveraging previous experiences and user expectations to optimize the functionality of related items
Why Understand the Process
The following stages typically take place in the UI/UX design process:
Project Initiation
A group of stakeholders, including design, product, technical, and business representatives, determines the project's objective, deliverables, and deadlines.
User Research and Evaluation
UI/UX designers employ a range of research techniques, including card sorting, surveys, and user interviews, to learn more about the issues that their target users experience and what they would need and want from a solution.
Identifying the Problem
The designer or designers identify the problem they will address based on the results of their investigation. This typically entails creating a problem statement that expresses the issue simply and effectively, providing the design team with a clear focus while coming up with ideas for solutions.
Designing the Product's User Interface
The process transitions to user interface design, which involves creating high-fidelity prototypes from wireframes and low-fidelity ones, complete with text, color, and necessary components like text entry fields, scrollbars, and buttons. These prototypes are interactive in their most elaborate iteration and simulate the final product's functionality.
Understanding Concept
This stage is primarily about ideation and developing possible solutions. Depending on the size and composition of the design team, it can be completed alone or in a group and typically includes hand-drawing preliminary concepts.
Creating a User Experience Design
The UX design process begins with a decision on a path. It considers the product's structure, layout, and organization while focusing on user actions for specific tasks. This includes defining user flows, specifying information architecture, and creating low-fidelity prototypes and wireframes.
Testing for Usability and Users
Validating concepts and designs on actual users is crucial to ensure they meet end-user needs and resolve issues. Designs are updated and refined based on customer feedback, but the integration of user testing depends on limited resources and time.
Additional Testing of Users and Usability
High-fidelity prototypes simulate the appearance and functionality of the final product. It's essential to conduct additional user/usability testing before development to make sure the designs are usable and accessible and contribute to the intended solution of the user problem.
Handoff to the Developers
The last stage is to give the designs to the developers. After that, the developers will code it and build a functional product that actual users can utilize after deploying it.
What Skills are Required for UI/UX Designers?
A wide range of soft skills, technical design expertise, and tool mastery are required of UI/UX designers. A few of the most essential skills for UI/UX designers are:
1. Design Thinking Process
The design thinking process is essential for UI/UX designers as their entire work focuses on imagining and making the designs work out in real life. This thinking process focuses on recognizing users' needs, generating imaginative concepts, and offering innovative solutions.
It seeks to build products or services that are intuitive, user-friendly, and successfully suit the needs of the users by putting the user at the center of the design process. Let's look at the steps of how the design thinking concept works:
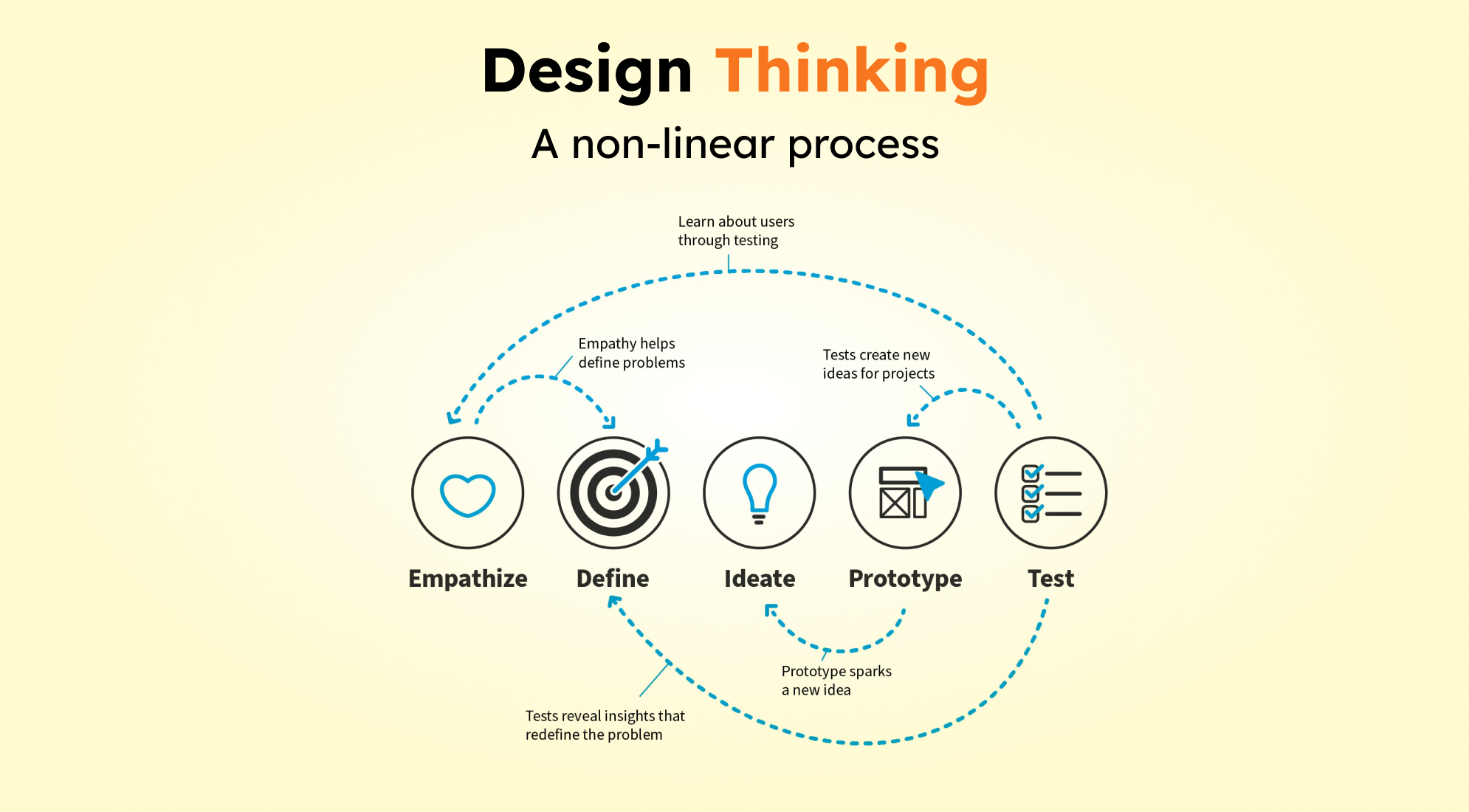
- Empathize: This process starts by comprehending the requirements, difficulties, and pain points of the users.
- Define: Then, define the problem statement or design challenge after they have a solid understanding of the users' needs.
- Ideate: After properly defining the problem, consider all the possible solutions and designs to resolve it.
- Prototype: Once you have an idea, create a rough version and then improve it. These prototypes could be interactive mock-ups or simple sketches and wireframes.
- Test: In order to obtain input and verify assumptions, real users test the prototypes.
2. User Research
UI/UX designers are required to have research skills in conducting several studies to collect, assess, and process both qualitative and quantitative data. Research is essential for UI/UX designers to build an impactful design that affects the users. Collecting data and inputs from different areas helps them make decisions that are user-centred and data-driven.
3. Understanding of Wireframe
Wireframing is the technique of drawing low-fidelity, simplified layouts that show a digital interface's hierarchy and structure. All brilliant designs start with a basic version. The refining and iteration process makes the basic design a top-notch one. So, UI/UX designers need to utilize wireframes to plan out user flows, content positioning, and important capabilities. It will help to concentrate on a product's general arrangement and structure and then fine-tune it.
4. Efficiency in Building Prototypes
UI/UX designers use prototyping software such as Sketch, Figma, or Adobe XD to produce interactive prototypes that mimic user interactions. During the prototyping process, interactive models of digital products are built to test and validate design concepts and interactions. This enables them to obtain input, optimize the user experience, and iterate on concepts prior to development.
5. Good Knowledge of visual design
Both UI and UX designers use visual design programs like Figma, Sketch, Photoshop, and Illustrator to produce a product's visual components. In addition to being proficient with the tools, you should increase your understanding of the best practices for visual design, including typography, color theory, layout, iconography, and general design theory.
6. Familiarity with UI/UX Design Patterns
Design patterns for user interfaces (UI) and user experiences (UX) provide uniform solutions to common design problems and help in the creation of recognizable, intuitive, and visually appealing interfaces. Here is a list of tools that every UI/UX designer should know to get new patterns and inspiration for UI/UX design:
- Mobbin Design: Mobbin Design, also known as Mobbin, aims to help aspiring designers find the best design patterns for iOS UI. It has assembled carefully selected clusters of the newest patterns from apps that showcase the best of design.
- Screenlane: Screenlane is a collection of tools that offers UI and UX designers a complete platform to assist them in making better design alternatives.
- Page Collective: Web designers and marketers can find insights and inspiration from Page Collective, an online hub devoted to landing page design trends and innovations.
7. Knowledge of Design Guidelines
UX designers may develop user-friendly, intuitive, and consistent interfaces with the help of a set of design standards and principles known as Human Interface Guidelines (HIGs). In UX design, they help to provide uniformity, guarantee accessibility, reduce effort and time, and promote creativity. The visual design features, interaction patterns, and usability considerations that are unique to a given platform or operating system are defined by these guiding principles. Google's material design is one of the examples of HIGs.
Google's Material Design is a widely used design language. It is a set of guidelines for an integrated framework of interaction, motion, and visual design that works with various device forms. Using this design language, UI and UX designers can produce more engaging and responsive digital experiences for their users.
Summing Up
UI/UX design is important for creating user-centric digital experiences. To provide a satisfying and interesting experience, designers consider users' tastes and behaviors, therefore making it easy for them to come up with smooth and simple layouts. The effort put into such precise results in more contented customers, improved conversion rates, and lower support costs. A well-structured interface encourages trust from consumers, hence making it a necessity for any forward-thinking companies within today’s competitive marketplace.
If you are looking for professionals to build a strong and impactful UI/UX design for your website, eCommerce platform, or anything else, Code Accelerator is here to help! From designing website/landing page mock-ups to building templates for email campaigns, we have everything covered to meet your user requirements. Connect with our experts today and share your requirements!
Still unsure which pack to choose for your business requirements? The Code Accelerator team can help you find the perfect HubSpot match for your organization. With our myriad expert HubSpot services, our skilled and experienced professionals will assist your business in investing in the right place. Share your requirements or queries with our team, and we'll connect with you as soon as possible to discuss the best possible solutions.





.webp)

%201.png?width=1016&height=912&name=image%20(54)%201.png)